There are multiple factors contributing to the development of this problem such as damage to the nerves, ligaments, tendons and bone fractures of the foot that can cause subluxation (partial dislocation of some joints).
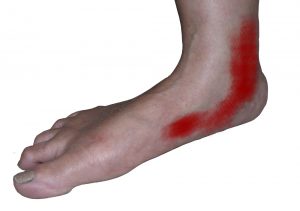 Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity has often been linked with dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. The loss of active and passive pull and elongation or rupture of the tendon alters the normal biomechanics of the foot and ankle. The reasons for this can be many and varied including; Diabetes , Rheumatoid Arthritis , age , injury and prolonged use of steroids.
Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity has often been linked with dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. The loss of active and passive pull and elongation or rupture of the tendon alters the normal biomechanics of the foot and ankle. The reasons for this can be many and varied including; Diabetes , Rheumatoid Arthritis , age , injury and prolonged use of steroids.
The problems experienced can include:-
- Pain and swelling along the medial (big toe) side of the arch and ankle area corresponding to the track of the posterior tibialis tendon which travels from the back of the leg under the medial ankle bone into the foot.
- Pain along the lateral (outside) edge of the foot.
- There may be pain at the end of the day or after long periods of standing.
- It may not be possible to do a one legged heel raise (while keeping the knee straight ).
- It may not be possible to participate fully in their normal activities or sports.
Treatment Options include:-
- Orthotics specifically designed to control the position of the foot, so keeping better foot and ankle alignment.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs may be helpful.
An off-the-shelf (prefabricated) shoe insert may work well in very mild cases. - Laced ankle boots ( like walking boots ) can give extra foot and ankle support .
Ankle support braces. - Shoe modifications to the sole to stabilize foot function.
- If conservative treatments are unsuccessful then surgery may be considered.



